Tufted hamster
Phodopus cristatus
The tufted hamster (P. cristatus) is a descendant of the Campbell's dwarf hamster. Its species diverged sometime ~12,000 years post-establishment.
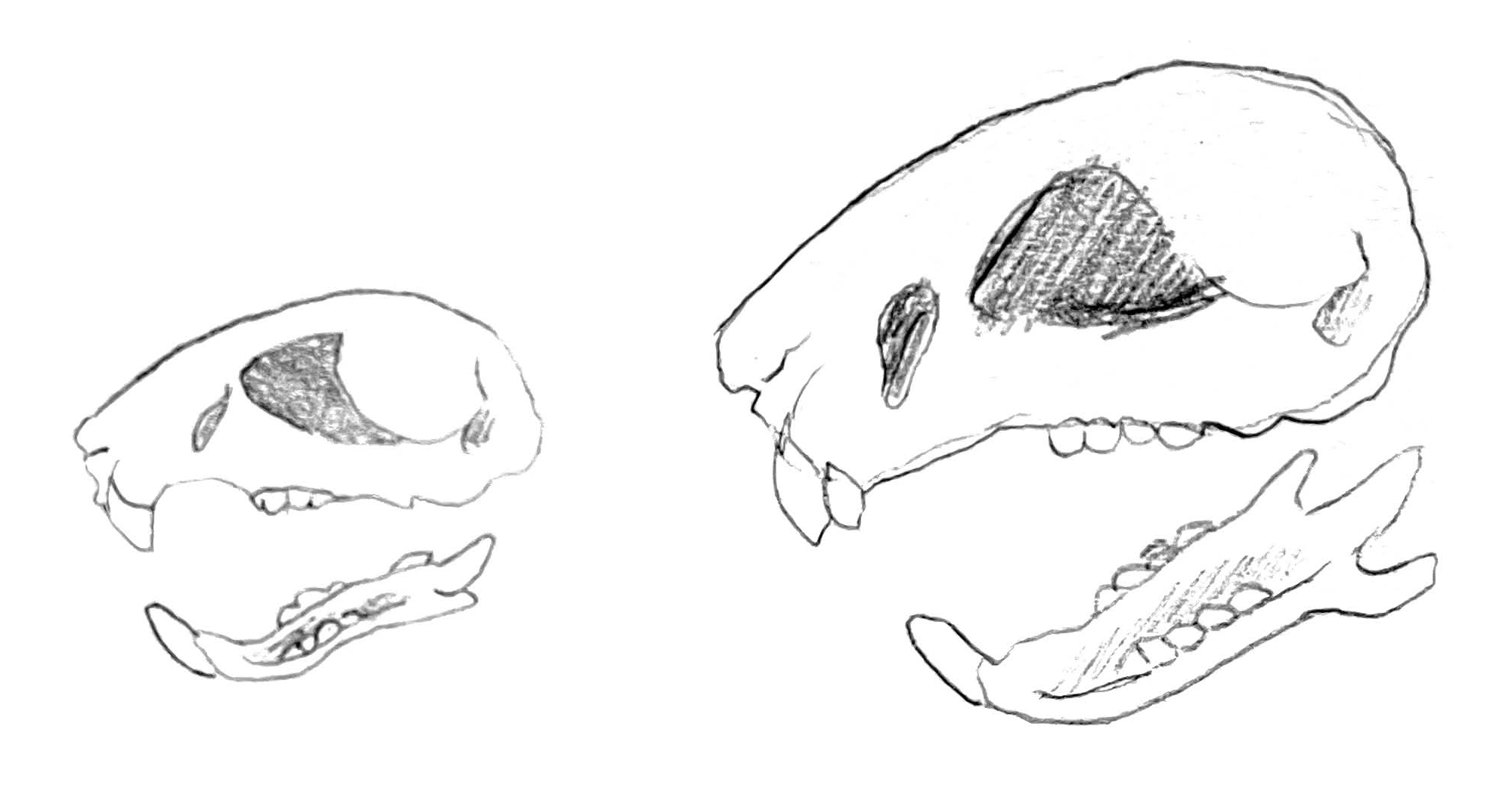
Description: Reaching about 20-30 centimeters in length and 930-1,400 grams in weight, the tufted hamster resembles a large Campbell's dwarf hamster with slightly longer legs, bigger jaws, a thicker pelt, and a longer tail. As its name implies, it also has a fuzzy tuft of fur sticking out of the top of its head. It can be found in a variety of colors and patterns, although gray-brown and white are the most common. Unlike the Campbell's dwarf hamster, it has an extra pair of upper incisors directly behind the first, as well as an additional pair of molars on both the top and bottom rows. Its cheek pouches are much smaller in size. Males are usually larger than females.
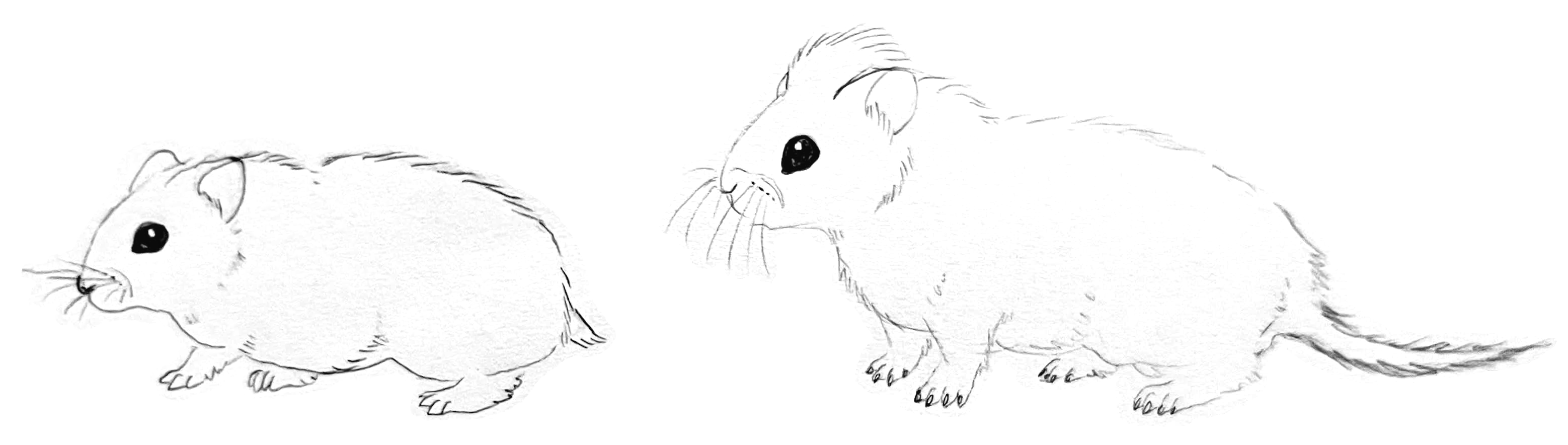

Diet: The majority of its diet consists of grass and larger leafy vegetations. Unlike its ancestor, it has no interest in eating insects.
Behaviour: It is diurnal, meaning it is awake during the day and asleep at night. It grazes during the warmest part of the day. It becomes more active as temperatures start to cool, foraging for other foods and patrolling its territory. It marks its territory with urine and feces, as well as rubbing its scent glands against objects. Males are very aggressive towards each other while females are more tolerant towards each other. Female tufted hamsters occasionally share the same territory if resources are plentiful.
Smaller, insect-eating species like to move into the dens created by the tufted hamster to keep them free of bugs. In its den, the tufted hamster will construct a nest out of soft plants, moss, and fur.
Reproduction: They are a promiscuous species. Unlike the Campbell's dwarf, the male tufted hamster does not help care for his offspring. A female tufted hamster will typically give birth to 3 or 4 litters per year, with an average of 4 pups per litter. The